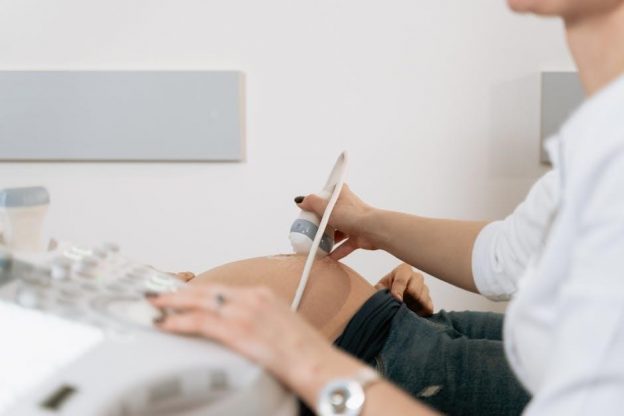
Ultrasound-guided hip injections are a precise, minimally invasive procedure using real-time imaging to target hip joint tissues, ensuring accurate delivery of therapeutic agents for pain relief and improved mobility.

Purpose and Types of Hip Injections
Hip injections aim to diagnose or treat joint pain, using therapeutic agents like corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid. Types include intra-articular injections for joint conditions and bursa injections targeting inflammation.
2.1. Diagnostic Injections
Diagnostic injections use local anesthetics to identify pain sources. Ultrasound guidance ensures precise delivery, helping confirm whether hip joint pain originates from the joint or surrounding tissues, aiding accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
2.2. Therapeutic Injections
Therapeutic injections deliver medications like corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid into the hip joint. Guided by ultrasound, these injections reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and improve joint function, offering targeted treatment for conditions such as osteoarthritis, bursitis, and tendinosis, enhancing patient mobility and quality of life.
2.3. Types of Injected Substances
Common substances used in ultrasound-guided hip injections include corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, hyaluronic acid for joint lubrication, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) to promote tissue repair. These agents are precisely delivered to target areas, ensuring optimal therapeutic effects and minimizing systemic side effects, tailored to the patient’s specific condition and needs.
Procedure Overview
Ultrasound-guided hip injections involve real-time imaging to precisely locate the injection site, ensuring accurate delivery of therapeutic agents into the hip joint or surrounding tissues, minimizing complications and enhancing outcomes.
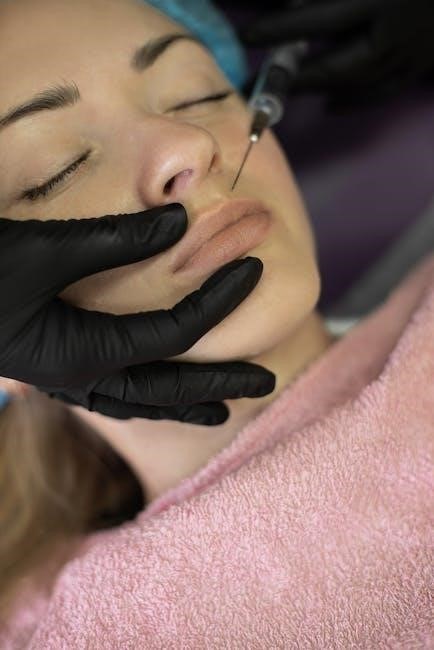
3.1. Patient Preparation
Patient preparation includes removing clothing to expose the hip area, ensuring skin cleanliness, and possibly fasting if sedation is planned. Comfort is maintained with a pillow under the knee during the supine position. No specific fasting is typically required unless general anesthesia is used, though guidelines may vary by clinic.
3.2. Positioning and Setup
The patient is positioned supine with the hip in neutral position, often with a pillow under the knee for comfort. The ultrasound probe is placed to visualize the hip joint, ensuring clear imaging. The setup involves preparing the skin with antiseptic solution and using real-time ultrasound guidance to optimize needle placement accuracy during the injection process.
3.3. Needle Placement and Injection Technique
Under ultrasound guidance, the needle is inserted through the skin and advanced towards the target tissue within the hip joint. The anterior sagittal approach is commonly used, ensuring precise placement. The injection is administered slowly, with continuous monitoring to confirm the distribution of the therapeutic agent and avoid complications, optimizing both safety and efficacy.

Role of Ultrasound in Guiding the Injection
Ultrasound provides real-time visualization of hip joint structures, enabling precise needle placement and avoiding neurovascular damage. It ensures accurate delivery of therapeutic agents without radiation exposure.
4.1. Real-Time Visualization
Real-time visualization via ultrasound allows direct observation of the needle and surrounding tissues during hip injections. This ensures precise placement of therapeutic agents into the target area, enhancing accuracy and minimizing risks. The dynamic imaging enables immediate adjustments, improving the effectiveness of the procedure while reducing potential complications. It is crucial for ensuring patient safety and optimal outcomes.
4.2. Avoiding Neurovascular Injury
Ultrasound guidance significantly reduces the risk of neurovascular injury by providing clear visualization of nerves, blood vessels, and surrounding soft tissues. This real-time imaging ensures precise needle placement, avoiding critical structures near the hip joint. By minimizing accidental contact with neurovascular bundles, the procedure enhances safety and reduces complications, leading to better patient outcomes and more effective treatment delivery.
4.3. Accuracy and Safety
Ultrasound-guided hip injections ensure high accuracy by providing real-time visualization, reducing complications and enhancing safety. This method minimizes the risk of misplacement, offering precise delivery of therapeutic agents. Compared to blind injections, ultrasound guidance significantly improves outcomes by ensuring the injection reaches the intended target, thus optimizing effectiveness and patient safety.
Indications for Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injections
Ultrasound-guided hip injections are primarily used to treat conditions like osteoarthritis, inflammatory arthritis, bursitis, and tendinosis, providing targeted relief for hip pain and improving joint function effectively.
5.1. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease, commonly affects the hip, causing pain and stiffness. Ultrasound-guided injections deliver hyaluronic acid or corticosteroids directly into the joint, reducing inflammation and improving mobility. This method is particularly effective for patients who do not respond to oral medications or prefer minimally invasive treatments. It helps alleviate symptoms and delays surgical interventions.
5.2. Inflammatory Arthritis
Inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, causes hip pain and swelling due to joint inflammation. Ultrasound-guided injections deliver corticosteroids directly into the joint, reducing inflammation and pain; This targeted approach minimizes systemic side effects and provides rapid relief, helping to preserve joint function and improve mobility in patients with inflammatory conditions.
5.3. Bursitis and Tendinosis
Bursitis and tendinosis involve inflammation of the bursae and tendons around the hip joint, causing pain and limited mobility. Ultrasound-guided injections deliver corticosteroids directly to the inflamed areas, reducing swelling and discomfort. This targeted approach helps alleviate symptoms, improve joint function, and restore range of motion, providing effective relief for patients with these conditions.

Contraindications and Risks
Ultrasound-guided hip injections may be contraindicated in patients with active infections, bleeding disorders, or allergies to injectable substances. Risks include infection, bleeding, or allergic reactions, though rare.

6.1. Absolute Contraindications
Absolute contraindications for ultrasound-guided hip injections include active joint or systemic infections, severe allergies to the injected substance, and presence of prosthetic joints. Additionally, patients with significant bleeding disorders or those on anticoagulant therapy are generally excluded due to heightened risks of complications. These conditions pose serious risks that outweigh potential therapeutic benefits, necessitating alternative treatments.
6.2. Relative Contraindications
Relative contraindications for ultrasound-guided hip injections include chronic kidney disease, uncontrolled diabetes, and compromised immune systems. Patients with recent joint trauma or those with a history of poor wound healing may also face increased risks. Additionally, pregnancy and concurrent use of certain medications, like immunosuppressants, require careful consideration to ensure safe and effective treatment outcomes.
6.3. Potential Complications
Potential complications of ultrasound-guided hip injections include infection, allergic reactions, and transient pain at the injection site. Rarely, nerve damage or bleeding may occur if nearby structures are inadvertently targeted; Proper technique and sterile conditions minimize these risks, ensuring a safe and effective procedure for most patients. Close monitoring post-injection is recommended to address any adverse effects promptly.
Comparison with Other Guidance Methods
Ultrasound-guided hip injections are compared with fluoroscopy, MRI, and blind techniques, highlighting their real-time imaging benefits, reduced radiation exposure, and improved accuracy for precise needle placement and therapeutic delivery.
7.1. Fluoroscopy-Guided Injections
Fluoroscopy-guided injections use real-time X-ray imaging to direct needle placement, offering precise visualization of bony structures. While effective for hip injections, they involve radiation exposure, unlike ultrasound. This method is particularly useful for complex cases but requires specialized equipment and training, making ultrasound a more accessible and safer alternative for many procedures.
7.2. MRI Guidance
MRI guidance provides high-resolution imaging for detailed visualization of soft tissues, making it ideal for complex hip injections. However, it is not typically used for real-time procedures due to its static nature. MRI offers precise pre-procedural planning but lacks the accessibility and cost-effectiveness of ultrasound-guided methods, making it less common in routine injections.
7.3. Blind Injections
Blind injections rely on anatomical landmarks without imaging guidance, reducing accuracy and increasing risks of neurovascular injury. They are less precise compared to ultrasound-guided methods, potentially leading to lower success rates and higher complication risks. This technique is often criticized for its lack of real-time visualization, making it less favorable in modern practice.

Effectiveness and Outcomes
Ultrasound-guided hip injections effectively reduce pain and improve joint function, offering both immediate and long-term relief. Patients often experience reduced reliance on pain medications and enhanced quality of life.
8.1. Pain Relief and Functional Improvement
Ultrasound-guided hip injections provide significant pain relief by delivering therapeutic agents directly to the affected area. This targeted approach minimizes systemic side effects and enhances functional improvement, allowing patients to regain mobility and resume daily activities more effectively. Improved joint mechanics and reduced inflammation further contribute to better overall outcomes and patient satisfaction with the treatment.
8.2. Reduction in Medication Use
Ultrasound-guided hip injections often lead to a reduction in medication use by effectively managing pain and inflammation at the source. Patients frequently experience decreased reliance on oral painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, minimizing potential side effects associated with long-term medication use. This approach supports a more sustainable and medication-free management of hip-related conditions, improving overall patient well-being and quality of life significantly.
8.3. Long-Term Benefits
Ultrasound-guided hip injections offer significant long-term benefits, including improved joint function and mobility. By addressing inflammation and degeneration, these injections can delay the need for surgical interventions. Patients often experience sustained pain relief, reduced inflammation, and enhanced quality of life, making it an effective treatment option for managing chronic hip conditions and improving overall well-being over time.
Safety and Complications
Ultrasound-guided hip injections are generally safe, with minimal complications when performed by skilled professionals. Proper technique minimizes risks, ensuring effective treatment while maintaining patient safety;
9.1. Common Side Effects
Common side effects of ultrasound-guided hip injections are typically mild and temporary. These may include pain at the injection site, swelling, or bruising. Some patients might experience a mild allergic reaction to the injected substance. Post-injection flare, a temporary increase in pain and inflammation, can occur but usually resolves within a few days. Proper post-procedure care minimizes these effects.
9.2. Rare but Serious Complications
Although uncommon, serious complications of ultrasound-guided hip injections include infection, nerve damage, or tendon rupture. Infection risk is low but can occur if sterility is compromised. Nerve injury is rare due to precise imaging but may cause temporary or permanent deficits. Tendon rupture is infrequent yet possible, especially with corticosteroid use. Adhering to guidelines minimizes these risks.
9.3. Post-Injection Care
After an ultrasound-guided hip injection, patients may experience mild soreness or swelling at the injection site. Rest and ice application are recommended to alleviate discomfort. Normal activities can typically resume the following day, though strenuous exercise should be avoided for 48-72 hours. Pain relief often begins within a few days, with full effects noticeable within one week.
Ultrasound-guided hip injections offer precise, effective pain relief and improved mobility, making them a valuable treatment option for hip-related conditions with minimal complications and lasting benefits.
10.1. Summary of Benefits
Ultrasound-guided hip injections provide precise delivery of therapeutic agents, ensuring accurate targeting and minimizing risks. They offer significant pain relief, improved joint mobility, and reduced inflammation. This method enhances treatment outcomes, lowers the need for pain medications, and supports faster recovery, making it a safe and effective option for managing hip-related conditions.
10.2. Future Directions in Hip Injection Techniques
Future advancements in ultrasound-guided hip injections may include improved imaging technologies, AI integration for enhanced precision, and the development of biologic therapies like PRP and HA. These innovations aim to further optimize treatment outcomes, reduce recovery times, and minimize complications, ensuring safer and more effective hip injection procedures.
